What are the Carotid Arteries?
The carotid arteries are large arteries located on either side of the neck. These arteries are responsible for delivering oxygenated blood to the brain. The right common carotid arteries are derived from the brachiocephalic artery, which then gives rise to the left and right carotid arteries. The left carotid arteries branch off the aorta, the body’s largest artery.
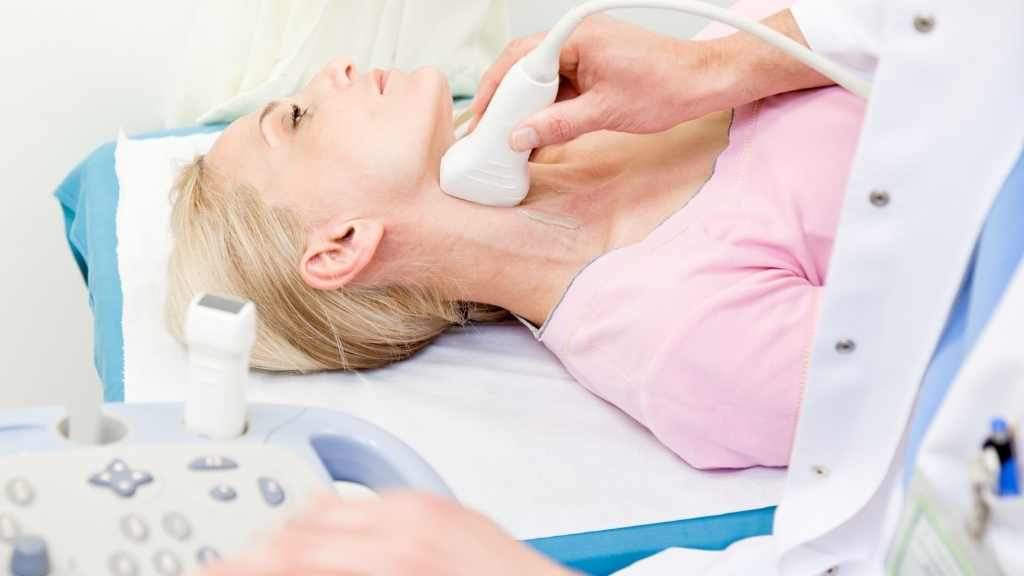
Carotid artery function can be affected by carotid artery disease. This is a common yet serious condition. Carotid artery disease occurs when a buildup of plaque within the arteries results in reduced blood flow or even a blockage. A carotid artery ultrasound screening is often recommended to diagnose any problems with the carotid arteries.
Carotid Artery Disease and Screening
A carotid artery ultrasound is a type of Doppler ultrasound exam. Doppler ultrasound exams use Doppler technology to create color images and videos of the veins and arteries using high-frequency soundwaves. The videos show both speed and direction of blood flow within the arteries, detecting potential blockages. Identifying these blockages early on is important because they can cause a stroke or even fatality.
Carotid artery disease is characterized by plaque buildup within the arteries, which is caused by excessive fatty deposits. Carotid artery disease can be serious because an interruption of blood flow to the brain can cause a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), which is similar and sometimes a precursor to a stroke. Symptoms of a stroke are usually sudden and include:
- Difficulty speaking or seeing
- Dizziness or severe headaches
- Numbness in the face or limbs, usually on one side of the body
There are a variety of risk factors for carotid artery disease. These include the following:
- Diabetes
- Family history
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Older age
- Sleep apnea
- Tobacco use
Carotid Artery Screening Process
A screening exam is designed to detect signs of disease before the onset of any symptoms. Carotid artery disease does not usually present symptoms until a stroke or TIA occurs. Screening can catch signs of carotid artery disease early on, but screening is usually only recommended in specific cases such as:
- Existing arterial conditions such as peripheral artery disease, coronary artery disease, or aortic aneurysm
OR - At least two risk factors for stroke such as high blood pressure, tobacco use, or family history
OR - Being 55+ years old with one or more risk factors for carotid artery disease
A carotid artery Doppler ultrasound exam is the best way to screen for carotid artery disease. Ultrasound exams are quick, painless, and noninvasive with no known side effects, making them a critical diagnostic tool. A Registered Vascular Technologist (RVT) usually performs a carotid artery ultrasound exam. RVTs have been trained to conduct vascular ultrasound exams. A typical carotid artery screening process proceeds as follows:
- The physician refers the patient for a carotid artery ultrasound exam.
- The patient visits the vascular lab for a carotid artery ultrasound. An RVT usually conducts the exam. The ultrasound machine consists of a console, a monitor, and a handheld device called a transducer. The transducer emits harmless soundwaves, and when pressed against the skin, the soundwaves penetrate the skin to create images of the veins and arteries.
- A trained physician interprets exam results and then sent to the referring physician for final review and diagnosis.
- The referring physician will review the results and recommend treatment as necessary.
Although the consequences of carotid artery disease can be serious, it is highly treatable. In fact, preventive measures for carotid artery disease are often the same as treatment recommendations and medication. These measures include a healthy lifestyle, limiting cholesterol and salt intake, not using tobacco, and exercising regularly. If you think you may be at risk for carotid artery disease, you must talk to your doctor and see if a carotid artery ultrasound screening is recommended.
Guest Contributor: Jordan Galerkin
Sources:
- Carotid Artery. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21492-carotid-artery https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/17607-arterial–venous-mapping
- Carotid Artery Disease. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/carotid-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20360519
- Carotid Artery Screening. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/screening-carotid
- Types of Ultrasound: Doppler vs. Duplex. https://www.ultrasoundquotes.com/blog/doppler-vs-duplex/
