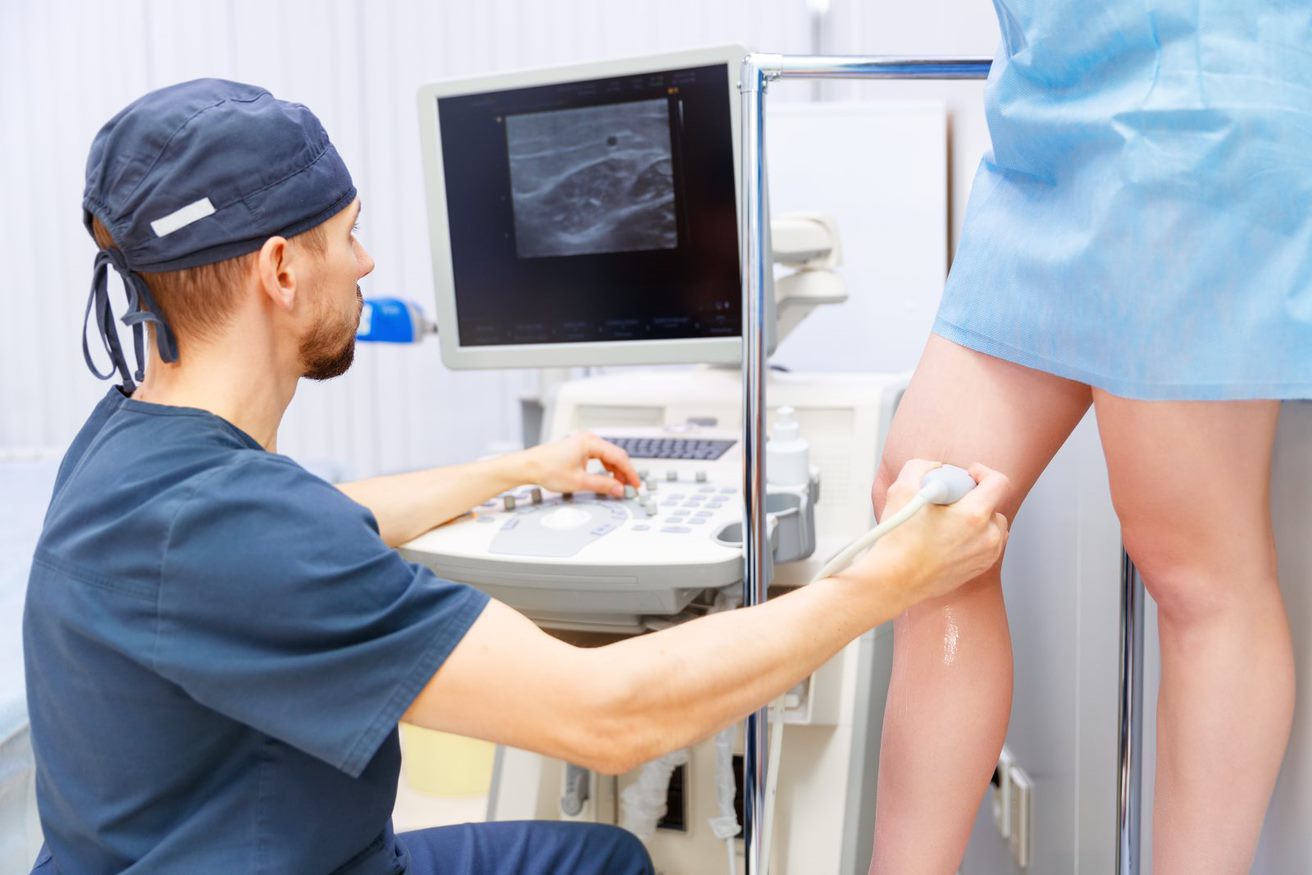
A venous ultrasound is a type of vascular ultrasound exam that uses Doppler technology to provide images of the veins and blood flow within the body. This type of ultrasound can be used to help diagnose a variety of conditions, including blood clots and deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that usually occurs in just one leg at a time, and it is caused by a blood clot forming within the vein that disrupts blood flow. Although DVT can have serious complications, it is highly treatable with early detection using a tool like venous ultrasound. For more information on DVT, click here.
A Doppler venous ultrasound exam uses harmless, high-frequency soundwaves to produce images of what is going on inside the body. Not only can it provide images of the veins, but it can provide information on the speed and direction of blood flow. This can be critical in determining if a blood clot is present. Blood clots can lead to an even more serious condition called pulmonary embolism (PE). PE occurs when a portion of the blood clot breaks off and becomes lodged in the lungs, causing lung damage and even death.
Venous ultrasound exams are a critical tool in early diagnosis for blood clots and related conditions. These exams are performed by Registered Vascular Technologists (RVTs) who are highly trained and certified to conduct ultrasound exams. The process of receiving a venous ultrasound is non-invasive and painless. The RVT can perform a diagnostic exam in a matter of minutes. The technologist will use a small handheld device called a transducer pressed against the skin to gently compress the veins. This allows them to see if there are any abnormalities such as stiffness in the veins or interrupted blood flow.
Sources:
- Venous Ultrasound. Radiology Info. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/venousus
- Venous Thromboembolism (Blood Clots). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/facts.html
- Deep Venous Thrombosis Ultrasound Evaluation. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470453/
